XR is the umbrella term for the entire “E(x)tended (R)eality” landscape.
The concept aligns and connects all aspects of immersive content, from virtual reality landscapes, to augmented reality applications.
Currently, demand for XR, in all its unique forms, is growing at an incredible rate. In the next five years, experts predict the space will be worth around $463.7 billion, with an amazing CAGR of over 62%. This number could easily extend to $905.7 billion by 2027.
Around 60% of people today believe XR will be a mainstream concept within the next 5 years. Countless companies have also begun experimenting with their own versions of XR, whether they’re building virtual reality collaboration rooms, or AR apps for customer service.
But what does extended reality really mean?
Let’s find out.
What is Extended Reality? Defining XR
XR, or Extended Reality, is the ecosystem of technology and tools dedicated to the creation of “immersive” environments. The purpose of XR is to use a combination of hardware and software to make people feel as though they’re in a different world.
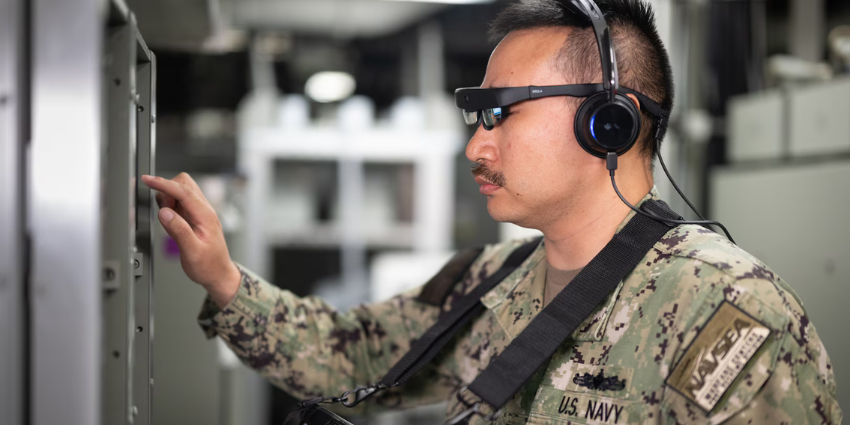
Such technologies have already begun to gain attention in the form of VR games for consoles, and AR applications for wayfinding and try-before-you-buy customer experiences. For businesses, XR allows interaction with rich content in a way that encourages creativity and growth. The result is higher customer engagement levels, a significant reduction in human error, and better team productivity.
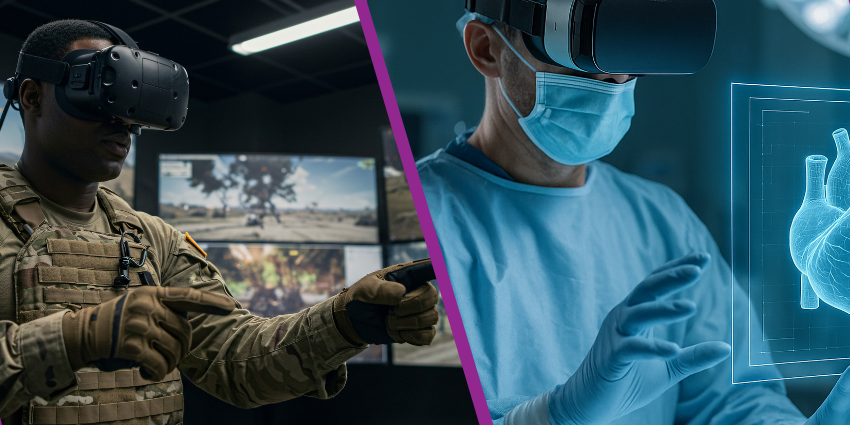
One of the major trends driving focus on XR today is the COVID-19 pandemic. When team members could no longer operate together in-person, they turned to things like mixed reality and VR for education and collaboration. Elsewhere, AR gave companies the opportunity to maintain rich human connections with customers without face-to-face interactions.
Extended reality covers concepts like:
- Computer vision and sensors
- Spatial sound and memory
- 360-degree feedback and haptic feedback
- Immersive content
- Agency in immersive software
The Components of Extended Reality: AR, VR and MR
As mentioned above, XR isn’t an immersive technology of its own, but an umbrella term used to describe all avenues of immersive tools. The three central technologies of XR today include:
Virtual Reality:
Virtual Reality involves using headsets to replace the vision of the wearer and feedback spatial sound for immersive experiences. With VR, the user’s environment is replaced by a virtual world, created in software. Haptic feedback and sensors process the movements and activities of the user in this environment, allowing them to interact with various pieces of content. In recent years, virtual reality has become a crucial part of the creative process for many companies and groups.
Bristol University used VR to assist with developing vaccines for COVID 19, and companies began using VR headsets as an alternative way to bring teams together on projects and discussions in a dispersed environment. VR offers a new landscape for collaboration and innovation.
Augmented Reality
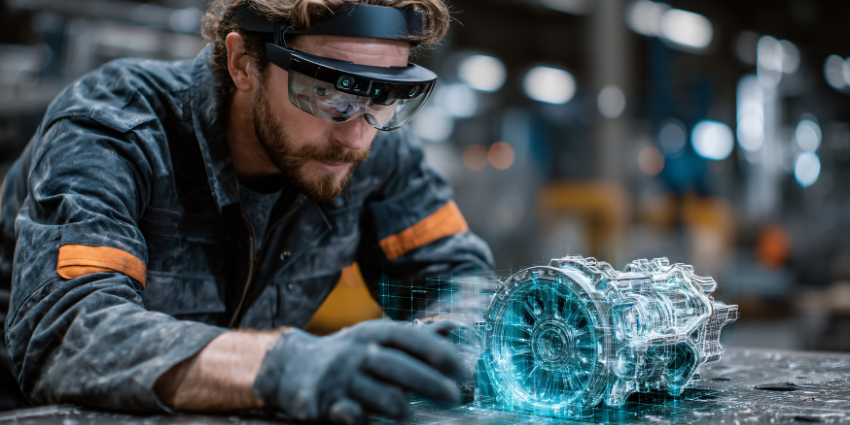
Augmented reality avoids simply replacing the physical environment, and instead aims to enhance your surroundings with new content. An AR application could bring a virtual version of a piece of furniture into a room so customers could see how it would look before spending money.
AR can also help with things like navigation by placing arrows on screens, or overlaying maps onto a person’s surroundings. Augmented reality is available through both smartphone applications, and visors or “smart glasses”. Most people regard AR to be the simplest and most accessible of the XR technologies, because it doesn’t always require a headset.
Mixed Reality
More than just a combination of AR and VR, Mixed Reality represents a new frontier for XR innovation. With Mixed Reality, people can bring holograms of their colleagues into their existing space and feel as though they’re sitting alongside their team members. Mixed Reality gives us the opportunity to interact with virtual content like never before.
Mixed Reality is one of the most exciting aspects of the MR environment, but it’s also an area that we have yet to do the most research in. Today’s companies are increasingly looking to Mixed Reality to solve a lot of the common problems with other forms of XR.
The Pros and Cons of Extended Reality
Extended Reality promises a new landscape of exploration and innovation for the modern world. As new technology emerges in haptic technology, and cognitive control, the potential of XR will only continue to grow. Some of the Pros and cons to consider right now include:
Pros
- Unlimited innovation: Visualizing and experimenting with 3D representations of products and blueprints allows for a much deeper level of creativity.
- Improved collaboration: Extended Reality can bring people together with a much more natural sense of presence than standard video or audio conferencing.
- Better learning: Access to contextual information, demonstrations, and 3D models allows for better more in-depth learning experiences in virtually all environments.
- Improved productivity and performance: In the XR environment, employees can work together on projects much faster and more efficiently than if they were sending emails back and forth.
- New opportunities: XR solutions give us the opportunity to explore new experiences like never before, from virtual events to digital vacations.
Cons:
- Privacy issues: A lot of people worry about the privacy issues associated with digital devices. XR technology needs to collect a lot of information about the user to operate well.
- Costs of implementation: High-quality XR experiences are expensive, particularly with headsets and haptic sensors to consider. Not everyone can afford to get involved.
- Physical safety: Stepping into a new virtual environment or augmenting your existing environment can make it harder to be aware of the dangers around you.
Where is the Future of XR Headed?
Extended Reality has the potential to impact every industry and transform the world as we know it. Already, metro Drivers are testing trains with VR headsets, and healthcare companies are opening new doors for the training of future doctors and surgeons. The headsets available for VR, AR, and MR technology are becoming increasingly impressive too, with better display quality, improved eye-tracking, and the ability to create immersive audio experiences too.
The rise of new hardware technology, combined with easier access to software tools for innovation means that opportunities in the XR environment are evolving at an incredible pace.
The future of technology starts with innovations like XR.